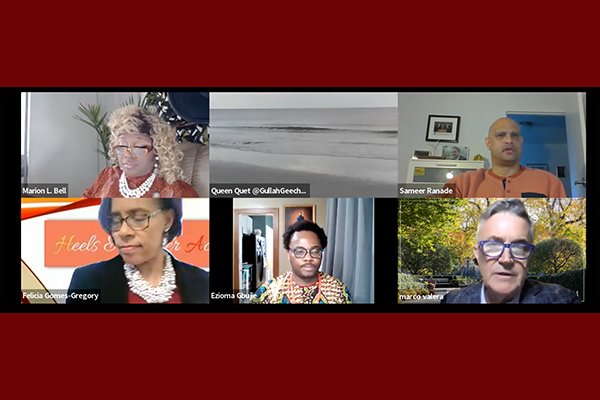
Fordham College at Lincoln Center graduate Marquetta L. Goodwine, Queen Quet of the Gullah/Geechee Nation, sang those lines from the spiritual “I’ve Been in the Storm Too Long” at the beginning of her presentation during an April 25 panel on environmental and climate justice. The event, held online, was sponsored by Fordham’s MOSAIC alumni affinity chapter and the Office of Alumni Relations. It featured alumni, faculty, and other experts who discussed how environmental and climate issues disproportionately affect certain populations—and how we can, both globally and locally, work toward lessening those impacts.
The lyrics Queen Quet sang also speak to the work she has been doing for more than two decades as chieftess of the Gullah/Geechee Nation, a sovereign people who live along the Atlantic coast from Pender County, North Carolina, to St. John’s County, Florida. On the low-lying land populated by the Gullah/Geechee, flooding has been a longstanding problem only heightened by the increasing number and severity of storms due to climate change.
As one of two keynote speakers, Queen Quet emphasized the importance of communicating about climate change in ways that are easily understandable to every community.
“It cannot be spoken of in terms of carbon emissions and CO2 and these types of things, because that is not everyday common vernacular throughout America,” Queen Quet said.

She also discussed some of the specific work the Gullah/Geechee Nation is doing to prepare for natural disasters caused by climate change, including building resiliency hubs to store supplies and solar power charging stations, which could also serve as an airdrop point for food and other necessities. And while her nation has already seen a great deal of damage from flooding and beach erosion, Queen Quet said that speaking at the U.N. Climate Change Conference in 2019 was an opportunity to share optimistic ideas with other leaders from around the world.
“We’re all trying to show each other living examples of what we’re doing where we are to make this world a better place, to try to heal it, try to reverse some of the impacts,” she said.
‘We Must Be Willing to Serve’
The second keynote speaker, Dr. Daniel Chidubem Gbujie, a climate activist, writer, and oral surgeon from Nigeria, seconded Queen Quet’s call for effectively communicating the risks of climate change to every community.
“Context matters,” he said. “The way you deliver your message is very important.”
Dr. Gbujie pointed to the ways that sub-Saharan Africa has already been devastated by climate change, from flooding in his native Nigeria to drought that has played a role in conflicts like the Sudanese Civil War, which in 2017 the U.N. World Food Program called “the first climate change conflict.”
As the founder of the Team 54 Project, a nonprofit organization with the goal of raising awareness about the impact of climate change and the need to take urgent global actions, Dr. Gbujie said that he has found inspiration in the mission of Jesuit education and the idea of cura personalis—care for the whole person—when thinking about how best to approach the climate crisis.
 “For everything that we experience here,” he said, “there’s a level of empathy and sympathy we have to have. To resolve the climate crisis we have right now, we must be willing to serve. …
“For everything that we experience here,” he said, “there’s a level of empathy and sympathy we have to have. To resolve the climate crisis we have right now, we must be willing to serve. …
We must be willing to look for new, innovative ideas, and we must be willing to ensure that we have a moral compass that guides us when we negotiate.”
Along with the keynote speakers, the panel—which was moderated by Marion Bell, FCLC ’92, one of MOSAIC’s co-founders, with support from fellow chapter co-founders Felicia Gomes-Gregory, FCLC ’88, GSAS ’98, and Marlene Taylor-Ponterotto, FCRH ’79—featured presentations from several speakers who discussed the infrastructural keys to adapting to and mitigating climate change, both at Fordham and beyond.
Using Infrastructure and Policy to Prepare for the Future
After opening the event with a prayer, Bell, who is also the chairperson for environmental and climate justice of the NAACP mid-Manhattan branch, introduced Marco Valera, vice president for administration at Fordham. Valera, who took on his current role in 2019 after serving as vice president for facilities management, discussed the work that has been done and will be done infrastructurally to reduce the University’s carbon emissions,—continuing to improve building insulation, for example, moving the University’s vehicle fleet to electric, and using available surface space for green roofs and solar panels, like those atop the Rose Hill regional parking garage.

The second speaker was Sameer Ranade, a climate justice adviser for the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority (NYSERDA), a public-benefit corporation whose mission is to “advance clean energy innovation and investments to combat climate change, improving the health, resiliency, and prosperity of New Yorkers and delivering benefits equitably to all.” Ranade’s position at the authority was created as part of the state’s Climate Leadership and Community Protection Act of 2019—which was signed into law at the Fordham School of Law—and he provides support for both New York’s Climate Action Council and the Climate Justice Working Group.
Ranade presented some of the state’s energy and climate justice goals, which include reducing statewide greenhouse gas emissions to 60% of 1990 levels by 2030 and to 15% of 1990 levels by 2050.
“Clean energy can actually lower emissions in all sectors, but especially so in buildings, transportation, and electric power generation,” Ranade said, noting that moving to clean energy would also add 10 jobs for every one job displaced, according to a study by the state’s Just Transition Working Group. He also encouraged audience members to attend one of the Climate Action Council’s remaining public hearings to share input on the scoping plan for New York’s climate goals.
Fordham professor John Davenport, Ph.D., discussed another element of mitigating the effects of climate change that is particularly important to New York and other coastal communities: managing stormwater runoff. As the danger of strong storms and flooding continues to increase, Davenport said, it will be essential to use infrastructure like green roofs and street trees to absorb water and limit runoff, and to provide tax incentives to land and building owners for implementing methods of runoff reduction.
“It’s going to be important to start using the language of savings,” Bell said in response to Davenport’s presentation, touching on the same need for good communication highlighted by the keynote speakers. “What it will save us rather than how much it will cost us.”
]]>We connected with some of the countless Rams bringing people together to repair and lift up their communities.
A Pro Runner Blows the Whistle on Abusive Training Culture
In 2013, at age 17, Mary Cain was one of the top runners in the world, the youngest U.S. athlete ever to compete on a World Championships team. But soon after joining Nike’s elite Oregon Project to train with head coach Alberto Salazar, her health and her promising pro career deteriorated.
Her coaches forced her to lose weight, which led to the loss of her period for three years and stress-related injuries, including five broken bones, Cain said.

“You don’t go from losing weight to breaking bones in two days, right? There’s usually this long period of time where there’s this physical deterioration,” Cain said at Fordham’s ninth annual Sports Business Symposium, held virtually on March 25. “Throughout the day, I just was more prone to having silly things, like headaches, to just being more hungry, to being a little bit more irritated as a result, and to just being visibly fatigued.”
She began to dread the sport she had loved since fifth grade. Her physical, emotional, and mental health began to spiral downward. She developed an eating disorder and began to cut herself and have suicidal thoughts.
“What once had been something that came naturally to me, this beautiful experience … suddenly became a slog,” Cain said. “The longer that I was in this really circular system, the more my body broke down.”
Cain completed one year at the University of Portland while training with the Oregon Project before transferring to Fordham’s Gabelli School of Business, where she earned a bachelor’s degree in 2019. After moving to New York, she kept training with the Nike project until 2016.
In a November 2019 video piece for The New York Times, Cain said the all-male coaching staff, led by Salazar, did not include a certified sports psychologist or certified nutritionist, and that Salazar had tried to put her on birth control pills to lose weight and harmed her mental health by berating her and humiliating her in front of her fellow athletes.
“Women in sports are treated harsher when it comes to body image,” she said during the Fordham symposium in March. “And I believe the reason is mostly societal—the expectation to be a lighter weight is more attached to [women’s] looks and their meaning. And it’s this really toxic culture that I think permeates professional sports.”
After Cain’s story came out, many other women supported her claims, including Kara Goucher, an Olympic distance runner who had trained under the same Nike program. Salazar denied the allegations of abuse, but several weeks before Cain’s story was published, he received a four-year ban from the sport for doping violations, and Nike had already shut down the Oregon Project.
In January 2020, Nike completed an internal investigation of Cain’s allegations of abuse, and her story helped Nike identify initiatives to “do better in supporting female athletes,” including increasing the number of women coaches in sports and investing in scientific research into the impact of elite training on women and girls.
Today, Cain is the New York City community manager for Tracksmith, a running apparel company. She runs professionally as a member of USA Track & Field and continues to call for reforms, including having teams provide mental health counselors and sports psychologists who are separate from the coaching staff.
She said her goal in sharing her story is to make sure that no other athletes, particularly female athletes, have to go through the suffering she did.
“I hadn’t known that the situation was bad until somebody [told me], ‘That is bad. That shouldn’t happen to you.’ It’s normalized,” she said.
“I realized I didn’t want any other person out there to … be self-loathing, beat themselves up, and have this incredibly negative experience because they were under an emotionally abusive coach and almost didn’t know it.”
—Kelly Kultys, FCRH ’15
A Gun Violence Survivor Works to Heal Social Divisions
Lamont Young knows something about forgiveness and bridging interpersonal divides.
In 1993, he almost died after being shot seven times in the chest—point blank—by an acquaintance who was high on PCP. But he later found the strength to forgive his assailant, and in doing so, he was inspired to pursue a lifelong path of helping others.
That path eventually led him to the Graduate School of Education, where he earned a master’s degree in mental health counseling in 2018.

Then he made a career move that led to a personal transformation. He went to work with UNITE, a national initiative co-founded by Special Olympics Chairman Timothy Shriver that seeks to help Americans overcome divisions, and he gained a new perspective.
“I went in with this psychological approach to addressing the human condition and suffering caused by racism and discrimination. I had a burning desire to promote human dignity and shed light on segregation and dehumanization, but I was so caught up in my head trying to find ways to address this,” he said.
“Once I met with the UNITE team, I had a spiritual awakening. I started to address them not from my mind or from my heart, but from my spiritual background. It was transformative to understand that in spite of it all, we have to love, we still have to forgive.”
Young and his mother, Glenda, are featured in The Call to Unite: Voices of Hope and Awakening (Penguin Life/The Open Field), published in March. The book contains an interview with them conducted by Shriver, who knew Young from a young men’s group he once led in New Haven, Connecticut.
“A mother who raises a son who can take on the hardscrabble and often fatal streets of New Haven and not only come through it but come through it with forgiveness and an open heart—that’s a mother I want to learn from,” said Shriver, who spoke about the power of personal transformation at Fordham’s 2019 commencement ceremony, where he received an honorary doctorate.
Shriver said the book’s common thread is that when we treat ourselves and others with dignity, we unlock potential, even during disagreements.
“This is hard emotional, spiritual, political work,” he said. “If you want a quick solution, this is the wrong place. But if you want the best solution, there’s only one way, and that’s to unite.”
In addition to conducting research on dignity and respect for UNITE, Young works with people experiencing homelessness in New Haven at Columbus House and provides psychotherapy at Reliant Behavioral Health Community Service.
And he has learned about some new dimensions of forgiveness. “You can transgress against yourself by not forgiving yourself for some of the things that you haven’t done or some of the time you haven’t spent with your loved ones before they left this Earth,” he said. “I found that very powerful, to understand how to love and forgive yourself in the midst of turmoil and grief in order to free yourself.”
—Patrick Verel, GSAS ’15
A Nonprofit Leader Rescues Food Waste to Relieve Hunger, Promote Community
As the president and CEO of Community Solidarity, Jon Stepanian runs the largest vegetarian hunger relief program in the country. It’s a nonprofit he hopes doesn’t exist in a generation or two.
“When we started, we wanted to build a structure where we could theoretically put ourselves out of business in the communities where we operate,” Stepanian said. “We want to make sure that there’s going to be no need for us in 30 to 40 years if the community itself can take care of these needs.”

Based on Long Island, Community Solidarity rescues food from being wasted at supermarkets and farms and distributes it to people at food shares across four locations on Long Island and one in Bedford-Stuyvesant, Brooklyn. Each area, he says, is at risk of being a “food desert,” where fresh, nutritious, affordable food is hard to find.
“We rescue food waste because it’s common sense—it’s cheap to do it. But on a more philosophical level, on a more economic level, this is why people in our communities are struggling. We see it as a fundamental problem in our system that’s making people in our community poor and hurting people overseas and also destroying our environment by producing large quantities of stuff that we don’t need,” he said.
“We’re trying to rescue a small portion of that waste and repurpose it for something good, like feeding our neighbors, but we’re also trying to expose the problem.”
Stepanian knew he wanted to focus on helping local communities after graduating from Fordham. As an undergraduate, he studied history and political science—and an internship at the United Nations and a stint working at the American Civil Liberties Union gave him perspective on working within the intergovernmental and nonprofit sectors. Shortly after college, he and his friends started a Food Not Bombs chapter on Long Island, occasionally setting up a food distribution table on weekends.
Before long, he realized he needed to create a more sustainable structure to keep the food distribution going. Community Solidarity, with its 501(c)3 nonprofit status, was born out of this realization, although Stepanian said that a nonhierarchical structure was important from the outset.
“When we decided to become a nonprofit, we said we wanted no lines of demarcation between who can volunteer and who can get food,” he said. “We wanted to make it so you wouldn’t be able to tell if someone’s volunteering or in need or both.”
In a 2018 TEDxNYU talk, Stepanian talked about what he called “the myth of scarcity,” and how a communal response can not only address hunger but also help to create a deeper sense of belonging among neighbors.
“We’re also trying to raise awareness by saying that we will, in 10 years, be the largest hunger relief organization in the country, and we’re doing it for a thousandth of the price that the food banks are doing it, all because of this waste,” Stepanian said.
“This is how abundant that system of waste is. We want to make it eye-opening for people.”
—Adam Kaufman, FCLC ’08
A Familiar Face Offers Financial Literacy Training to Fellow Women of Color
As a young woman growing up in Brooklyn, Felicia Gomes-Gregory knew she wanted two things: to attend Fordham University and to work as a computer scientist. She achieved both.
But now, more than 30 years later, Gomes-Gregory is focused on something new, which she calls her passion project: Heels and Higher Achievement, a nonprofit that empowers women and people of color by helping them learn about finance.

Her path to forming the nonprofit started in 2016, when she received what she calls a blessing in disguise. After a decades-long career at various financial firms in New York City, she was laid off from Neuberger Berman, an employee-owned investment management firm.
She asked herself what she would do next. “In my heart, I’ve always wanted to … get more women involved in technology or finance, and especially women of color, because I never saw anybody that looked like me—or not enough of it,” Gomes-Gregory said.
She kicked off Heels and Higher Achievement (HHA) in 2018, determined to make financial literacy fun while giving a voice to those in her community who are empowering young women in tech, finance, STEM, media, or “whatever it is that they want to do,” she said. “I wanted to create a forum so that people can speak, but mainly speak about financial education.”
That first year, she conducted in-person workshops at schools, churches, and “anywhere anyone would hear me,” Gomes-Gregory said. She’d speak about basic financial literacy concepts and invite people to schedule a complimentary financial review—a kind of “GPS of your money,” she said, “to make sure you can stop working for money at some point and [let]money work for you.”
She also launched an ambassador program to give young girls opportunities to network with professionals and serve their communities through volunteer work. But COVID-19 meant pivoting to online events and workshops in 2020.
In April, HHA sponsored its second annual series of online workshops for Financial Literacy Month, including, for the first time, programming for men. “[Because] of all of the things that were happening in the Black community— between George Floyd, the social issues, COVID—men need to talk, too,” she said.
The digital programming has gone well, she said. She’s hoping to launch a YouTube channel and resume in-person events soon.
“I’m learning that self-care and self-preservation—from a financial, physical, mental, and spiritual [standpoint]—are so very important,” she said. “And I didn’t learn this until I was 50. So, now I’m teaching all of the young ’uns. ‘Take care of yourself first. You’re important.’”
—Sierra McCleary-Harris
Students Share Their Expertise with Bronx Businesses
When the pandemic upended everything in March 2020, Rich Shrestha was working on a research project about consumer behavior in the Bronx. As the economy went into a tailspin, his mind went back to his childhood in New Haven, Connecticut, where his father ran a Subway franchise for a decade.
“I saw him always grinding away every day, putting in 12-hour days. So, I can sympathize with the small business owners who are trying to survive in the age of COVID,” he said.

Shrestha, a rising senior majoring in economics at Fordham College at Rose Hill and a member of the University’s Social Innovation Collaboratory, reached out to friends he thought might be interested in helping small businesses.
Diontay Santiago, then a senior majoring in marketing at the Gabelli School of Business, was one of those who answered the call. In June 2020, they launched the Fordham Business Development Collaboratory. The student-run group, comprising more than 70 members, is split into teams that assist clients with finance, marketing, compliance, technology, and communications. Students offer their advice free of charge, relying on lessons they’ve learned in classes. They also conduct research, develop industry reports, and create case studies and videos for Bronx businesses.

For Santiago, who graduated from Fordham in May and had served as president of ASILI, the Black Student Alliance, the group has been a way to lift up the borough he has called home his whole life. “Doing this sort of thing weds the school to its actual geographic location and allows it to give back to the community it’s inhabited for the last two centuries or so. So when Rich presented me with the opportunity to work with him, I jumped at it.”
The group’s clients have included restaurants, nonprofits, a software company, and an insurance firm. In addition to word-of mouth and its website (fordhambdc.org), the group has connected with clients through the South Bronx Overall Economic Development Corporation.
Sadibou Sylla, the interim director of Fordham’s Social Innovation Collaboratory and an adjunct professor at the Gabelli School, said that all who contribute to the group personify what it means to be a “changemaker.”
“They understand that it is only in serving all that we serve ourselves,” he said, “and that business is nothing but an instrument for helping society.”
Shrestha is optimistic that the group will live on long after he and his classmates graduate.
“This is an opportunity to gain an understanding of the community you’re in, and how we can be a better part of it and better neighbors,” he said. “I think a lot of students are starting to realize how important that is.”
—Patrick Verel, GSAS ’15
Do you know a Fordham “Changemaker”?
Who are the unsung Rams working to foster collaboration and change in your community? Tell us about the people whose stories you’d like us to share. Write to us at [email protected].
Her path to forming the nonprofit started in 2016, when she received what she calls a blessing in disguise. After a decades-long career at various financial firms in New York City, she was laid off from Neuberger Berman, an employee-owned investment management firm.
She asked herself what she would do next. “In my heart, I’ve always wanted to … get more women involved in technology or finance, and especially women of color, because I never saw anybody that looked like me—or not enough of it,” Gomes-Gregory said.
She kicked off Heels and Higher Achievement (HHA) in 2018, determined to make financial literacy fun while giving a voice to those in her community who are empowering young women in tech, finance, STEM, media, or “whatever it is that they want to do,” she said. “I wanted to create a forum so that people can speak, but mainly speak about financial education.”

That first year, she conducted in-person workshops at schools, churches, and “anywhere anyone would hear me,” Gomes-Gregory said. She’d speak about basic financial literacy concepts and invite people to schedule a complimentary financial review—a kind of “GPS of your money,” she said, “to make sure you can stop working for money at some point and [let]money work for you.”
She also launched an ambassador program to give young girls opportunities to network with professionals and serve their communities through volunteer work. But COVID-19 meant pivoting to online events and workshops in 2020.
In April, HHA sponsored its second annual series of online workshops for Financial Literacy Month, including, for the first time, programming for men. “[Because] of all of the things that were happening in the Black community— between George Floyd, the social issues, COVID—men need to talk, too,” she said.
The digital programming has gone well, she said. She’s hoping to launch a YouTube channel and resume in-person events soon.
“I’m learning that self-care and self-preservation— from a financial, physical, mental, and spiritual [standpoint]—are so very important,” she said. “And I didn’t learn this until I was 50. So, now I’m teaching all of the young ’uns. ‘Take care of yourself first. You’re important.’”
]]>